Physical Characteristics

Sun vs mercury – The Sun and Mercury, two celestial bodies within our solar system, exhibit striking differences in their physical characteristics. These variations stem from their distinct origins, compositions, and positions relative to each other.
Like the celestial dance of the sun and Mercury, the clash between the United States and Uruguay on the football field promises to be an enthralling spectacle. As the sun’s fiery rays illuminate the celestial sphere, so too will the skills and passion of these two footballing giants light up the pitch.
The outcome of this match, like the enigmatic relationship between the sun and its closest planet, remains shrouded in uncertainty. But one thing is for sure, the battle between the Stars and Stripes and the Celeste will be a celestial event not to be missed.
Size and Mass, Sun vs mercury
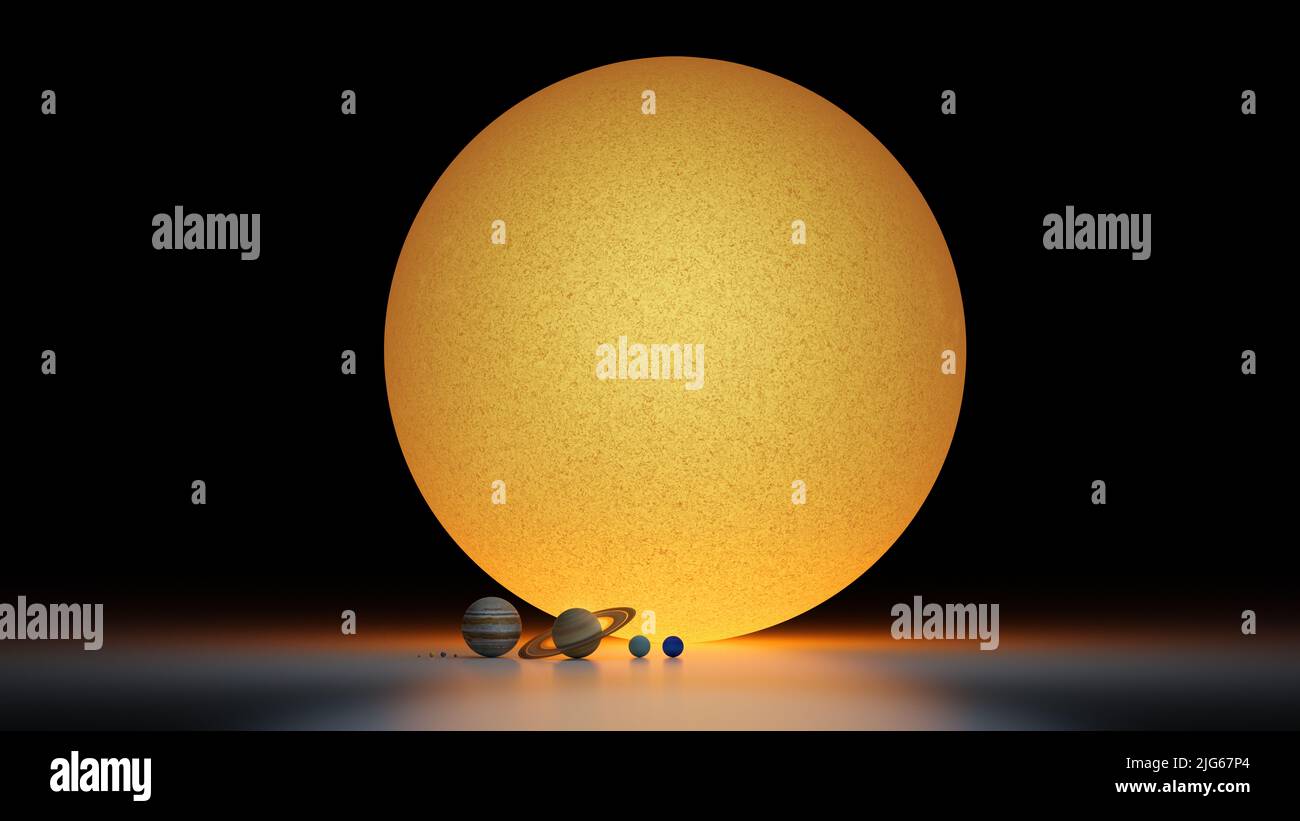
- The Sun is a colossal star, dwarfing Mercury in size and mass. Its diameter measures approximately 109 times that of Mercury, while its mass is a staggering 330,000 times greater.
- Mercury, in contrast, is a relatively small and rocky planet. Its diameter is a mere 4,880 kilometers, making it the smallest planet in our solar system.
Density and Volume
- The Sun’s immense mass and relatively large volume result in a comparatively low density of 1.41 grams per cubic centimeter.
- Mercury, despite its smaller size, possesses a higher density of 5.43 grams per cubic centimeter due to its compact, iron-rich core.
Surface Temperature and Composition
- The Sun’s surface temperature soars to a staggering 5,778 Kelvin (5,505 degrees Celsius), emitting intense radiation and light as a result of nuclear fusion reactions occurring at its core.
- Mercury, on the other hand, experiences extreme temperature variations due to its lack of an atmosphere. During the day, its surface temperature can reach up to 450 degrees Celsius, while at night, it can plummet to -180 degrees Celsius.
- The Sun is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, with trace amounts of heavier elements. Mercury, on the other hand, consists mainly of iron and silicate materials.
Atmosphere and Magnetic Field
- The Sun possesses a vast and dynamic atmosphere, known as the corona, which extends millions of kilometers into space.
- Mercury, in contrast, has an extremely thin and tenuous atmosphere, composed primarily of oxygen, sodium, and potassium.
- The Sun generates a powerful magnetic field that extends far beyond its surface, influencing the behavior of charged particles in the surrounding space.
- Mercury has a weak magnetic field, approximately 1% the strength of Earth’s, which is thought to be generated by its rapidly rotating iron core.
Orbits and Rotation: Sun Vs Mercury
The Sun, as the center of our solar system, governs the celestial dance of its celestial bodies. Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, exhibits unique orbital characteristics that set it apart.
Orbital Periods and Distances
The Sun, being a star, does not orbit any other celestial body. Mercury, on the other hand, completes one orbit around the Sun every 88 Earth days. This swift journey results in a shorter year on Mercury compared to Earth. The average distance between Mercury and the Sun is approximately 57.9 million kilometers, making it the closest planet to our star.
Eccentricity
The Sun’s orbit is nearly circular, with an eccentricity of almost zero. Mercury, however, has a more elliptical orbit, with an eccentricity of 0.206. This eccentricity means that Mercury’s distance from the Sun varies significantly throughout its orbit. At its closest point, Mercury is only 46 million kilometers from the Sun, while at its farthest point, it is about 70 million kilometers away.
Rotational Periods
The Sun rotates on its axis once every 27 days. This slow rotation gives rise to the sunspots that appear on its surface. Mercury, on the other hand, has a very slow rotation, taking 59 Earth days to complete one full rotation. This means that a single day on Mercury is equivalent to almost two months on Earth.
Axial Tilt
The Sun has no significant axial tilt, meaning its axis of rotation is nearly perpendicular to its orbital plane. Mercury, however, has a very slight axial tilt of about 2 degrees. This tilt contributes to Mercury’s extreme temperature variations, as different parts of the planet receive more or less sunlight at different times of its orbit.
Historical and Scientific Significance

The Sun and Mercury have captivated the curiosity of astronomers and scientists throughout history. Their observations and studies have led to groundbreaking discoveries about our solar system and beyond.
The Sun, as the central star of our solar system, has been revered and studied since ancient times. Early civilizations recognized its importance as a source of light, heat, and life. The development of telescopes in the 17th century allowed astronomers to observe sunspots and solar flares, providing insights into the Sun’s dynamic nature.
Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, has also been a subject of scientific interest. Its proximity to the Sun makes it challenging to observe, but advancements in space exploration have enabled scientists to gather valuable data. The first spacecraft to visit Mercury was Mariner 10 in 1974, followed by MESSENGER, which orbited the planet from 2011 to 2015.
Ongoing Missions and Future Plans
Currently, the Parker Solar Probe is conducting unprecedented close-up observations of the Sun, providing insights into its atmosphere and magnetic field. Future missions, such as the Solar Orbiter and the Dragonfly mission, aim to further explore the Sun and its impact on the solar system.
The study of Mercury continues with the BepiColombo mission, a joint venture between the European Space Agency and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. Launched in 2018, BepiColombo is scheduled to arrive at Mercury in 2025 and study the planet’s surface, magnetic field, and composition.
In the cosmic dance of celestial bodies, the Sun, our radiant star, dwarfs the diminutive Mercury. As their celestial ballet unfolds, our gaze shifts to the terrestrial realm, where the Brewers and Rockies prepare for their baseball clash. Like the cosmic waltz, the brewers vs rockies prediction is a tantalizing spectacle of skill and strategy.
Yet, even as the diamond lights illuminate the players, the celestial symphony of the Sun and Mercury continues its eternal rhythm, a reminder of the cosmic tapestry in which we are but fleeting actors.